What is an IP?
An IP address is a string of numbers separated by periods. Each of the decimal numbers in an IP address is called an octet.
octet = byte
So, for an IP address of 192.168.1.7, the first octet is 192, the second octet is 168, and so on.
Each number in the set can range from 0 to 255.
| 124 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | =255 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | =255 |
Octet
Example:
IP 192.168.18.161
if we convert the first octect to binary:
192 >= 128 = YES -> 192 - 128 = 64 64 >= 64 = YES -> 64 - 64 = 0 0 >= 32 = NO 0 >= 16 = NO 0 >= 8 = NO 0 >= 4 = NO 0 >= 2 = NO 0 >= 1 = NO
| 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 128 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
the result will be: 192 = 11000000
putting all the pieces together.
| 192 | 168 | 18 | 161 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11000000 | 10101000 | 00010010 | 10100001 |
Classes of Networks
Each calss determines
- Default network mask
- IP range
- Host Quantity
- Number of Networks available of that class
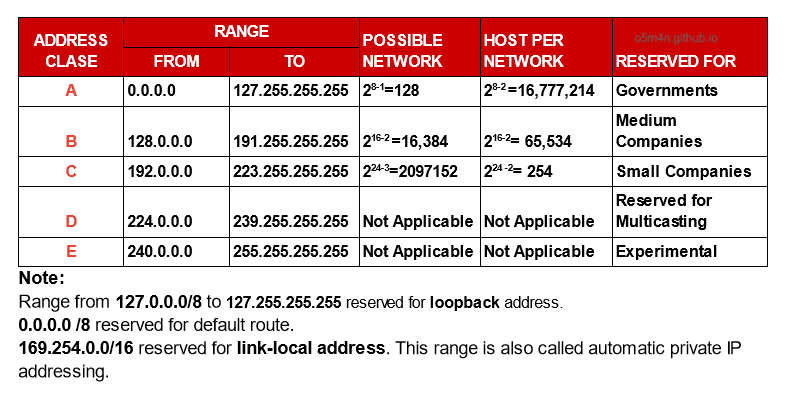 IP RANGE TABLE
IP RANGE TABLE
Multicast = An IP multicast serves to transmit data to multiple hosts.
loopback = Any traffic that a computer program sends on the loopback network is addressed to the same computer.
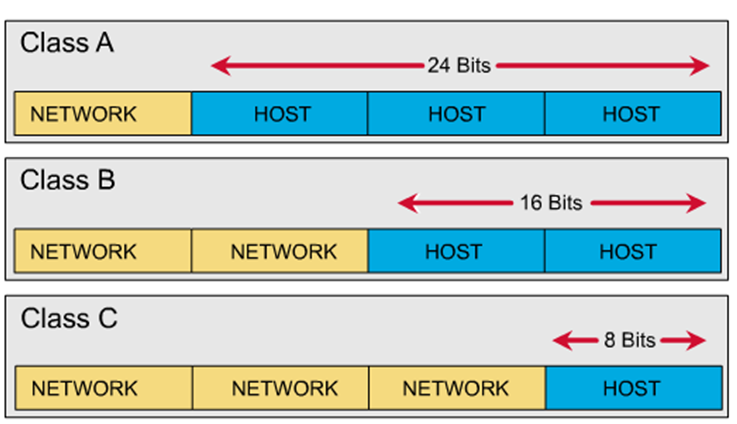 NETWORK-CLASS
NETWORK-CLASS
- The network part will not changed
- It is not possible to subnet an already subnetted network. that is, an address without class
- When it is an address with its default mask, it is an address with class.
- When subnetting it becomes a classless address
IP is subdivided into three types
Network Address
- The Network address identifies the specific network to which host is attached.
- It is the prefix that all equipment must have (Routers, Switches, etc ).
| 172 | 16 | 0 | 0 | IP TYPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10101100 | 00010000 | 00000010 | 00000000 | NETWORK ADDRESS |
| NETWORK | NETWORK | HOST | HOST | NETWORK ADDRESS |
Host Address
- Host address uniquely identifies a host within a network.
- It is the suffix that varies and is assigned to host
| 172 | 16 | 0 | 1 | IP TYPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10101100 | 00010000 | 00010010 | 00000001 | HOST ADDRESS |
| NETWORK | NETWORK | HOST | HOST | HOST ADDRESS |
Broadcast Address
- Used by ARP to query all network members
| 172 | 16 | 255 | 255 | IP TYPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10101100 | 00010000 | 11111111 | 11111111 | BROADCAST ADDRESS |
| NETWORK | NETWORK | HOST | HOST | BROADCAST ADDRESS |
Subnet Mask
Note:
- subnet mask is the one that determines the network class.
For example if they give me the address:- 255.0.0.0 indicates that it is a class A.
- 255.255.0.0 indicates that it is a class B.
- The remaining zeros are the ones that will be assigned to the HOST.
| 255 | 255 | 0 | 0 | IP TYPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11111111 | 11111111 | 00000000 | 00000000 | SUBNET MASK |
| RED | RED | HOST | HOST | SUBNET MASK |